What is a Standard Hydrogen Electrode
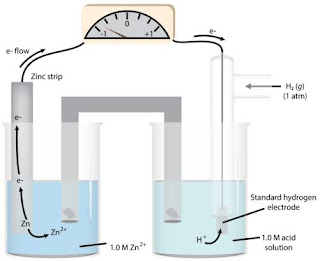
What is a Standard Hydrogen Electrode? The Standard Hydrogen Electrode is regularly shortened to SHE, and its standard terminal potential is proclaimed to be 0 at a temperature of 298K. This is on the grounds that it goes about as a source of perspective for correlation with some other anode. The redox half cell of the SHE is the place where the accompanying response happens: 2H+ (aq) + 2e–→ H2 (g) The response given above by and large happens on a platinum anode. The weight of the hydrogen gas present in this half cell approaches 1 bar. Utilization of Platinum in the Standard Hydrogen Electrode Platinum is utilized in the Standard Hydrogen Electrode because of the accompanying reasons: Platinum is a moderately dormant metal which doesn't consume without any problem. Platinum has synergist characteristics which advances the proton decrease response. The outside of platinum can be covered with platinum dark, a fine powder of pla...

