Redox Reactions
Redox Reactions
Redox represents decrease oxidation. An increase of electrons is a decrease. Lost electrons is an oxidation.
Decrease of species A: reactant A + e-→ item A
Oxidation of species B: reactant B → item B + e-
The conditions above are half-conditions. The entire condition for a redox response is acquired by adding the half-conditions.
The Redox Potential
On the off chance that the reactants in a redox response are blended in a similar vessel, they will deliver items in a similar vessel - decrease and oxidation happen in a similar vessel.
Nonetheless, the reactants can be part in an electrochemical cell, with the goal that the decrease and oxidations reactions happen independently. This permits us to locate their individual commitments to the response, including Gibbs free energies.
The redox potential is an electric likely estimated in volts.
Since 1 volt is indistinguishable from 1 joule for every coulomb, at the nuclear level the redox potential can be considered to gauge the energy change per electron moved.
The redox capability of a half-response is estimated versus a reference cathode half-response whose redox potential is appointed an estimation of 0 volts.
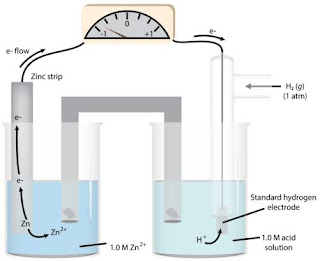
electrochemical cell
Hardware to gauge the decrease potential
of a half-response contrasted and a known half-response.
Redox potential is offered the hint E. In the event that it is a standard redox potential, it is offered the hint Eo.
Composing the Redox Potential
Redox possibilities are estimated for half-reactions. By show they are constantly composed as decreases, in any event, for oxidation reactions. Half-cells that go through decrease are appointed positive possibilities, while those that go through oxidation are relegated negative possibilities.
For instance, the standard redox potential for fluorine, which has a high liking for electrons, is positive. The standard redox potential for lithium, which loses electrons, is negative. Note how the lithium response is composed as a decrease.
F2(g) + 2e-⇌ 2F-Eo = +2.87 V
Li+ + e-⇌ Li Eo = - 3.04 V
Positive Redox Potentials
Positive redox possibilities demonstrate the response will in general continue from left to right. The higher the worth, the more noteworthy the inclination. Here are three instances of half-reactions with positive redox possibilities:
F2(g) + 2e-⇌ 2F-Eo = +2.87 V
Cl2(g) + 2e-⇌ 2Cl-Eo = +1.36 V
Au+ + e-⇌ Au(s) Eo = +1.69 V
Gold particles have a high fondness for electrons and thus are handily diminished back to metallic gold.
Negative Redox Potentials
Negative redox possibilities demonstrate the response will in general continue from option to left; the higher the total worth, the more prominent the inclination. Here are three instances of half-reactions with negative redox possibilities:
Li+ + e-⇌ Li Eo = - 3.04 V
Mg2+ + 2e-⇌ Mg Eo = - 2.37 V
Al3+ + 3e-⇌ Al Eo = - 1.66 V
E mentions to you what will be Reduced or Oxidized
You can utilize E or Eo qualities to anticipate the result of a redox response. This functions admirably whether the response is an electrochemical response in two half-cells or a compound response in a solitary vessel.
By and large, the half-condition with the more sure redox potential will be the decrease response and the other will be the oxidation.

Comments
Post a Comment